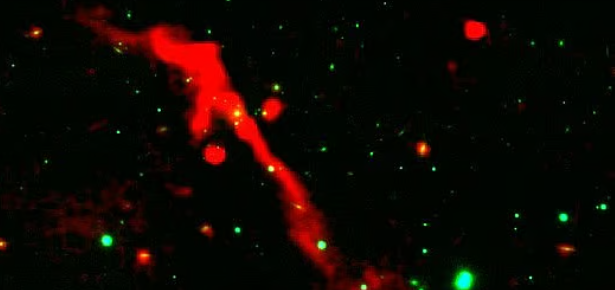
Astronomers have captured the awakening of a newly formed supermassive black hole, breaking a 100 million-year silence. The image shows the black hole exploding like a cosmic volcano. The explosion is so powerful that it has the power to change the shape of an entire galaxy.
While all galaxies have giant black holes at their centers, few produce such dazzling explosions of superheated plasma. This flame of cosmic lava stretches for about a million light-years. This flame is 10 times wider than our Milky Way galaxy. Scientist Shobha Kumari said about the black hole, it is like a cosmic volcano waking up again after a long period of quiet.
The black hole, J1007+3540, is located inside a massive galaxy cluster filled with extremely hot gas. There, a constant battle is going on between the explosive power of the black hole and the immense pressure of the surrounding galaxies. The information about this black hole has been published in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
According to scientists, data on the black hole has been collected using the Low Frequency Array in the Netherlands and the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope in India. When an object falls into the black hole, it becomes extremely hot due to friction. At one stage, this energy becomes quite strong. Then the black hole starts throwing jets or flames of superheated plasma into space. Radio images show that these jets are being bent and compressed by the pressure of the surrounding gas. Like volcanoes on Earth, this black hole has a long and violent history of eruptions. Scientist Shobha Kumari said that the location of the new jet inside the old layer proves that it is an irregular AGN or the central engine of this galaxy is turned on and off repeatedly over cosmic time.
The black hole in our own galaxy, Sagittarius A*, is currently dormant. Scientists believe it could reawaken in the future. If the flare from such an explosion were to hit Earth directly, it would be enough to wipe out all life on Earth. But that’s unlikely to happen before the Milky Way collides with our neighboring galaxy, the Large Magellanic Cloud, in about 2.4 billion years.
Source: Daily Mail